Laryngology
Vol. 45: Issue 5 - October 2025
Office-based transnasal injection laryngoplasty with cross linked hyaluronic acid in unilateral vocal fold palsy: long-term results
Abstract
Objective. To assess long-term phonatory outcomes of office-based injection laryngoplasty with cross-linked hyaluronic acid (HA) via transnasal flexible endoscopic phonosurgery (FEPS), followed by voice therapy, in patients with unilateral vocal fold palsy (UVFP).
Methods. Retrospective study on 20 UVFP patients treated with HA via FEPS within 6 months from diagnosis. All underwent postoperative voice rehabilitation. Voice outcomes were assessed at baseline (T0), and at 3 (T1), 12 (T2), and 24 (T3) months using
Maximum phonation time (MPT), Cepstral Peak Prominence Smoothed (CPPS), Acoustic Voice Quality Index (AVQI), GRBAS rating scale, and Voice Handicap Index-10 (VHI-10).
Results. MPT, CPPS, and AVQI improved significantly at T1, remaining stable at T2 and T3. GRBAS scores showed marked improvement at T3. Videolaryngostroboscopy confirmed better glottic closure and vocal fold vibration. VHI-10 scores decreased consistently, indicating reduced voice handicap.
Conclusions. FEPS-guided HA injection is a safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment for UVFP, ensuring lasting voice improvements, especially when performed early and combined with voice therapy. This strategy may reduce the need for open surgery in selected cases.
Introduction
Unilateral vocal fold palsy (UVFP) is a pathological condition characterised by the unilateral immobility of one vocal fold, resulting in varying degrees of voice impairment, dysphagia, and dyspnoea, which collectively can have a profound negative impact on the patient’s quality of life 1.
The aetiology of UVFP is diverse, encompassing several potential causes. Surgical trauma, particularly from procedures involving the thyroid, cervical spine, or thoracic cavity, remains the leading cause of UVFP. Non-surgical causes include viral infections such as herpes simplex virus, neoplastic processes involving the mediastinum or neck, and neurogenic disorders like stroke or multiple sclerosis. Idiopathic UVFP is diagnosed when no cause is evident after extensive evaluation, accounting for a significant proportion of cases. A study by Rosenthal et al. provided a comprehensive longitudinal analysis of the aetiological factors associated with UVFP over a period of 20 years, encompassing data from 827 patients 2. The key findings indicate a substantial increase in the proportion of UVFP cases attributed to surgical procedures, which rose from 23.9% in the period from 1985 to 1995 to 46.3% in the period from 1996 to 2005. Conversely, the proportion of UVFP cases due to malignancies has declined significantly, decreasing from 24.6% to 13.5%. Specifically, lung malignancies, once a major cause of UVFP, have decreased from 19.6% to 6.6%. The study also highlights a relative stability in the incidence of idiopathic UVFP, which remains a significant category, accounting for 17.6% of cases in the most recent cohort, slightly up from 19.6% in the earlier period.
The objective of treating UVFP is to restore effective vocal function and address glottal insufficiency. Current treatment strategies for UVFP encompass three main approaches: surgical interventions 3, speech therapy 4, and observation. The choice of management is typically determined by various factors including the presence of aspiration, the extent of nerve injury, findings from stroboscopy, the patient’s vocal requirements, existing comorbidities, and the patient’s preferences and concerns. Based on these considerations, patients with UVFP may receive one or a combination of these treatment options.
Historically, management strategies have favoured a conservative approach, waiting up to 12 months for potential spontaneous recovery before considering invasive procedures like injection laryngoplasty (IL). However, recent findings suggest that early intervention with intracordal injections may significantly improve patient outcomes in terms of voice quality and recovery, and also decreases the likelihood of requiring subsequent more invasive surgeries, such as thyroplasty 5.
IL is a minimally invasive procedure for treating UVFP, presenting low risks compared to open laryngeal surgery and first described by Brünings in 1911 6. IL has evolved over time with various injection materials like collagen, polydimethylsiloxane, autologous fat, calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA), and hyaluronic acid (HA) 7. Cross-linked HA was introduced as injection material by Hertegard et al. in 2002 8, and finds its greatest potential in non-immunogenic properties and effectiveness in mimicking the viscoelastic characteristics of healthy vocal folds. Despite multiple brands and varying molecular sizes of HA, it remains a common choice for IL due to its safety and efficacy, though injection techniques and outcomes vary in the literature 9.
Current practice entails a variety of surgical approaches for ILs. Augmentations can be performed both by direct microlaryngoscopy under general anaesthesia and by transoral, percutaneous, or transnasal approaches under local anaesthesia. Injection procedures in awake patients can be conducted in office, representing valid, low cost, and minimally invasive solutions for vocal fold augmentations 3,10. Among office-based procedures, transnasal endoscopic injections represent a feasible and effective option, as described by Ricci Maccarini et al. 10. In particular, the technique called flexible endoscopic phonosurgery (FEPS) encompasses the use of an operative rhinolaryngoscope to perform laryngeal surgical procedures under local anaesthesia and allows the surgeon to have a functional check of the operated larynx in real time 11.
The present retrospective study aims to describe long term phonatory outcomes of IL performed with cross-linked HA through FEPS. To the best of our knowledge, the present is the first long term investigation on transnasal vocal fold augmentations in patients treated with cross-linked HA for UVFP in office.
Materials and methods
Patients and procedures
Twenty patients (10 males and 10 females) were selected from the records of an existing database of patients in follow-up for various voice pathologies. Selection criteria were: diagnosis of UVFP in intermediate position, unsatisfactory voice outcome − despite a regular speech therapy rehabilitation − according to a multidimensional analysis based on aerodynamic, electroacoustic, perceptual, self-assessment and endoscopic evaluations; phonosurgical IL performed in office, with cross-linked HA, through FEPS, within 6 months from diagnosis. Mean age was 62 ± 14 years, and mean time from diagnosis was 4.3 ± 1.3 months. All procedures were performed between January 2020 and December 2021. Sociodemographic and clinical features of the sample are shown in Table I.
The selected patients underwent in office IL with cross-linked HA (Restylane, Galderma SA, Zug, Switzerland) through FEPS under local anaesthesia, using a Karl STORZ flexible operative rhinolaryngoscope (KARL STORZ SE & Co. KG, Tuttlingen, Germany) and 23-gauge 120 cm long flexible endoscopic needles (Jiangsu Kangjin Medical Instrument Co. LTD, Zhenglu Town, Changzhou, China). The needle was connected to a 3 ml luer lock polycarbonate Medallion® syringe (Merit Medical Systems Inc, South Jordan, Utah, USA) filled with HA and mounted on a high-pressure injection gun (Medtronic Inc, Dublin, Ireland) modified by Ricci Maccarini and De Rossi 19, as shown in Figure 1.
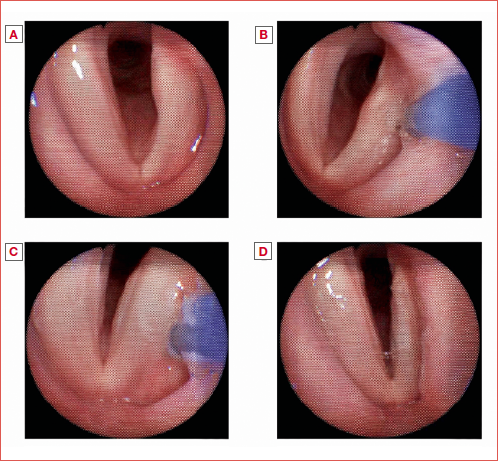
Oro-nasal local anaesthesia was performed through the nebulisation of lidocaine spray before the procedure. Each patient was in a sitting position, with a peripheral venous access, blood pressure and oxygen saturation levels monitoring. When a mild sedation was required, 1 or 2 mg of intravenous midazolam were administered, according to individual needs. Glottic plane anaesthesia was obtained by the irrigation of lidocaine solution through a catheter inserted into the operative channel of the endoscope. Once a good level of local anaesthesia was obtained, the IL was performed. The amount of injected material was 1-1.5 ml HA according to specific needs. Injections were performed into the paraglottic space and the sites of injections were the posterior third of the vocal fold (in order to obtain intra-rotation of the vocal process of the arytenoid), and the middle third of the vocal fold (in order to obtain filling and augmentation of the vocal fold body).
No intra- or postoperative complications were registered in the cohort. An example of IL performed through FEPS is shown in the Cover figure.
Each patient underwent a transnasal fibre endoscopic evaluation at 7 days after surgery in order to check the immediate postoperative course and exclude post-surgical complications. Each patient then underwent a voice rehabilitation protocol of 2 months, aiming at consolidating glottic competence. Time points for voice outcome evaluations were at 3, 12, and 24 months after surgery.
All the following assessments were carried out before phonosurgery (T0), and at 3 months after surgery (T1), 12 months after surgery (T2), and 24 months after surgery (T3).
Voice analysis
Voice signals were recorded respecting standard conditions, with a Samson Meteor Mic (Samson Technologies, Hauppauge, NY) placed at a distance of 30 cm from the mouth of the patient in a quiet environment (< 40 dB), connected via USB to a MacBook Pro computer (Apple, Cupertino, CA) running PRAAT software (Version 5.3.57 for Mac, Boersma & Weenick, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands). Audio files were digitised on 16 bit at sampling frequency of 48 kHz.
Maximum phonation time (MPT) was measured through the window selection of the longest of three sustained /a/. Acoustic voice quality was assessed through the smoothed Cepstral Peak Prominence Smoothed (CPPS) 12 and the Italian version 03.01 of the Acoustic Voice Quality Index (AVQI) 13,14, calculated on 6 seconds of concatenated continuous speech (cs) and the sustained vowel (sv) /a/. As suggested by the AVQI Italian validation study, 25 syllables of phonetically balanced sentences were used for continuous speech.
Perceptual assessments were carried out through the GRBAS rating scale, based on the recorded voice samples (both sv and cs). The GRBAS scale is a widely used perceptual evaluation tool specifically addressing the following parameters of voice quality: grade (G), roughness (R), breathiness (B), asthenicity (A) and strain (S) 15,16. Each parameter scores from 0 (normal voice) to three (severe dysphonia). Auditory-perceptual judgements were performed by a blinded expert and trained listener.
Videolaryngostroboscopy
Videolaryngostroboscopies (VLS) were performed with an Olympus Evis Exera II 18 endoscopy system and an Olympus ENF VH trans-nasal flexible endoscope (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Patients were asked to produce some sustained /i/ and the following parameters were assessed: glottic closure (A); amplitude of vocal folds vibration (B); periodicity of glottic vibration (C); supraglottic framework behaviour (D). Each parameter was evaluated and scored according to the VLS parameters form as suggested by Ricci Maccarini et al. 17.
Self assessments
Each patient completed the Italian Voice Handicap Index 10 (VHI-10) 18, a validated and robust tool to assess the patient’s self perception of a voice problem. Its score ranges between 0 and 40; the higher the score, the greater the perceived voice handicap.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out with GraphPad Prism software (Version 10.0). Means and standard deviations (SDs) for continuous variables were calculated. The normality of the distributions was assessed with the D’Agostino Pearson Test. Voice variables before and after phonosurgical approaches and voice therapy were calculated and compared. Friedman tests with Dunn’s post hoc corrections for multiple comparisons and ANOVA tests with Tukey’s post hoc corrections for multiple comparisons were used to detect statistical differences between the various checkpoints, as appropriate. Correlation analysis was carried out with the Spearman r coefficient. An alpha of 0.05 was considered for the statistical procedures.
Results
Acoustic-aerodynamic analysis
Means and SD for MPT were 4.5 ± 1.8 seconds at T0; 6.3 ± 3 seconds at T1; 8.8 ± 4.8 seconds at T2 and 8.6 ± 5.8 seconds at T3, as shown in Figure 2. Significant differences were found between T0-T1 (p = 0.042), T1-T2 (p = 0.0002), and T2-T3 (p = 0.0014).
Means and SD for CPPS and AVQI are shown in Figure 3. CPPS values were 7.9 ± 3.3 dB at T0, 12.4 ± 2.5 dB at T1, 13.1 ± 1.9 dB at T2, 13.2 ± 2.4 at T3. AVQI scores were 6.6 ± 2.5 at T0, 3.6 ± 1.8 at T1, 3.1 ± 1.3 at T2, 2.9 ± 1.7 at T3. Significant differences were found both for CPPS and AVQI between T0 and T1 (p < 0.0001), T0-T2 (p = 0.0001) and T0-T3 (p = 0.0001). No significant differences were found between T1-T2 and T2-T3 nor for CPPS or AVQI.
Perceptual analysis
Means and SD for the GRBAS rating scale are shown in Table II. All the subscales showed significant differences. In particular, post hoc tests showed significant differences between T0 and T1 for the subscales G (p = 0.0045), B (p = 0.0036), A (p = 0.0004); between T0 and T2 for the subscales G (p = 0.0014), R (p = 0.007), B (p < 0.0001), A (p < 0.0001), S (p = 0.0087) and between T0 and T3 for the subscales G (p < 0.0001), R (p = 0.0001), B (p < 0.0001), A (p = 0.0009), and S (p = 0.0007). No significant differences were found for any subscale between T1-T2 and T2-T3.
Videolaryngostroboscopies
No spontaneous vocal fold motility recoveries were registered in the study sample during follow-up assessments. Means and SD for the videolaryngostroboscopic variables are shown in Table III. All the investigated parameters except for the variable D “supraglottic framework behaviour” showed significant differences. In particular, post hoc tests highlighted significant differences between T0 and T1 for the variables A “glottic closure” (p = 0.0007) and B “amplitude of vocal fold vibration” (p = 0.0029); between T0 and T2 for the variables A (p < 0.0001), B (0.0045) and C “periodicity of glottic vibration” (p = 0.007); between T0 and T3 for the variables A (p < 0.0001); B (p = 0.0005), C (p = 0.035). No significant differences were found for any considered variable between T1-T2 and T2-T3.
Self assessments
Means and SD for the VHI-10 questionnaire were 24.90 ± 5.26 at T0, 13.05 ± 6.85 at T1, 12.75 ± 6.32 at T2, 12.55 ± 8.21 at T3. One-way ANOVA showed significant differences between T0 and T1, T0 and T2, T0 and T3 (p < 0.0001). No significant differences were found between T1-T2 and T2-T3.
Gender, age and aetiology influence on voice outcomes after IL
Statistical analysis showed no significant correlations between the age of the patients and the variation of each investigated outcome parameter across T0-T3. Similarly, no significant difference was detected for any of the outcome variables between males and females, nor between post-surgical UVFP and other causes of UVFP.
Discussion
The current study examined the long-term phonatory outcomes of IL with cross-linked HA through FEPS in patients with UVFP. The findings provide significant insights into the efficacy of this procedure over a 2-year follow-up period.
The results of the acoustic-aerodynamic analysis showed notable changes in MPT, which increased significantly at 3-month follow-up (T1) compared to baseline (T0). However, MPT gradually decreased at 12 and 24 months (T2 and T3), though it remained significantly above preoperative values. This trend suggests that while cross-linked HA provides immediate and substantial augmentation, the gradual resorption of the material over time might correlate with a slight decline in MPT. Nonetheless, the sustained improvement compared to baseline highlights the effectiveness of the procedure in enhancing glottal closure, even in the long term.
Similarly, the improvements in the CPPS and AVQI were significant at 3 months, with stable results at the 12- and 24-month follow-ups. Furthermore, the perceptual assessment using the GRBAS scale showed improvements across all parameters, particularly in reducing roughness, breathiness, and asthenia, which are common indicators of dysphonia in UVFP. Videolaryngostroboscopic evaluations revealed improvements in glottic closure and vocal fold vibration amplitude, particularly in the early post-operative period. These results corroborate the acoustic findings, indicating that HA injections not only improve vocal fold bulk but also enhance vibratory function, contributing to better phonatory outcomes. The lack of significant changes in the supraglottic framework behaviour suggests that a certain amount of vestibular constriction might be functional for the maintenance of a satisfactory glottic competence.
VHI-10 results also reflected these improvements, with significant reductions in perceived voice handicap at all postoperative checkpoints. These findings underscore the positive impact of early intervention on patients’ perceived quality of life, particularly in mitigating the social and psychological burden of UVFP.
The analysis of gender, age, and aetiology on voice outcomes suggests that these factors have limited impact on the treatment results in this study. No significant correlations were observed between these variables and voice outcome parameters, indicating that IL with cross-linked HA via FEPS may be broadly effective across diverse patient demographics. However, these findings were derived from a relatively small sample size, limiting the generalisability of the conclusions.
When contextualised within the literature, these results align with current evidence suggesting that early IL can significantly reduce the likelihood of requiring more invasive procedures, such as medialisation thyroplasty 5. Numerous studies have confirmed that early medialisation of the vocal fold − particularly within 6 months of UVFP onset − capitalises on the synkinetic reinnervation process, which helps maintain the paralysed vocal fold in a more favourable paramedian position 5,19. Postoperative voice therapy also plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of patients with UVFP following IL. A study on the efficacy of voice therapy following IL highlighted that patients who underwent structured therapy post-surgery exhibited greater improvements in vocal quality and self-assessed voice handicap compared to those who did not receive therapy 20. Early initiation of therapy is particularly advantageous, as it enables patients to consolidate proper glottic competence while the injected material provides medialisation, facilitating better long-term voice outcomes.
Concerning surgical techniques, literature reveals that both local and general anaesthesia approaches provide comparable voice outcomes. A systematic review of IL procedures performed in office under local anaesthesia versus general anaesthesia in the operatory room found no significant differences in terms of post-procedural voice improvement 21. Therefore, the choice of the technique should be guided by patient tolerance and procedural considerations rather than expected differences in outcome. The use of local anaesthesia within FEPS in this study offers the advantage of real time voice assessment during the procedure, further supporting its efficacy as a minimally-invasive, office-based option.
Regarding the choice of injection material, there remains no clear consensus in the literature on the superiority of one material over another 7. As suggested by Kwon et al. the ideal injection material should be biocompatible, biomechanically similar to vocal fold components, easily injectable through a fine needle, readily available with minimal preparation time, applicable in an outpatient setting, easily removable in the event of revision surgery, and resistant to absorption or migration 22.
While cross-linked HA has been suggested to offer favourable biomechanical properties and safety, showing easy injection localisation, tissue compatibility, and residence time 23, other materials such as calcium hydroxyapatite, autologous fat, and collagen also provide viable alternatives 9,22,24. A recent study by Miaśkiewicz et al. compared 24-month voice outcomes after IL with calcium hydroxyapatite or HA in patients with UVFP and found no long-term differences in voice outcomes or number of reaugmentations with calcium hydroxyapatite compared to HA 25. Each material has its advantages, but the use of partially or fully resorbable materials, such as HA, is often preferred in early interventions due to concerns that permanent materials may interfere with potential spontaneous recovery 9. The present study’s use of cross-linked HA demonstrates its efficacy in achieving long-term voice improvement, particularly when followed by timely voice rehabilitation.
One of the primary limitations of this study is the relatively small sample size, which may affect the generalisability of the findings. While the results provide valuable insights into the efficacy of cross-linked HA injection via FEPS, larger studies are needed to validate these outcomes across a more diverse patient population. Additionally, the absence of a control group or comparison with other treatment modalities restricts the ability to definitively assess the superiority of this technique. Lastly, two-year follow-up, though sufficient to evaluate long-term phonatory results, may not fully capture the sustainability of the treatment’s benefits. Future studies should address these limitations by including larger cohorts, control groups, and extended follow-up periods to strengthen the evidence base.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the results of this study demonstrate the long-term efficacy of office-based IL using cross-linked HA by a FEPS approach in treating UVFP. The study reinforces the importance of early intervention in UVFP management: timely IL offers significant long-term phonatory benefits and might reduce the need for more invasive surgical interventions. Moreover, the combination of this procedure with early and consistent voice therapy maximises the likelihood of sustained improvement in vocal function. These findings, consistent with the existing literature, support the use of cross-linked HA as an effective and easy-to-use material for UVFP treatment by FEPS, particularly when early intervention is possible.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author contributions
MF: study design, surgical procedures, data collection, drafting the article, final revision; ARM, MS, MB, FP, GS, EC: drafting the article, final revision, surgical procedures.
Ethical consideration
All procedures performed in this retrospective study were in accordance with the requirements of the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant/patient for study participation and data publication.
History
Received: April 4, 2025
Accepted: July 15, 2025
Figures and tables
Figure 1. Instrumentation required for the injection laryngoplasty. Operative rhinolaryngoscope (A); flexible endoscopic needle connected to the injection gun (B); irrigation catheter connected to the syringe filled with lidocaine solution (C).
Figure 2. Representation of mean values and standard deviations of MPT at T0, T1, T2 and T3.
Figure 3. Representation of mean values and standard deviations of CPPS (left) and AVQI (right) at T0, T1, T2 and T3.
| No. patients | 20 |
| Age (years) | 62 ± 14 |
| Gender, N (%) | |
| Male | 11 (55%) |
| Female | 9 (45%) |
| Distance from diagnosis (months) | 4.3 ± 1.3 |
| Side of vocal fold palsy, n (%) | |
| Left | 12 (60%) |
| Right | 8 (40%) |
| Aetiology, n (%) | |
| Iatrogenic | |
| Thyroidectomy | 6 (30%) |
| Upper lung lobectomy | 1 (5%) |
| Vagal chemodectoma excision | 1 (5%) |
| Cardiothoracic surgery | 1 (5%) |
| Lateral neck dissection | 1 (5%) |
| Prolonged oro-tracheal intubation for COVID-19 | 4 (20%) |
| Idiopathic | 3 (15%) |
| Neurogenic | 3 (15%) |
| Subscale | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | Test | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mean and SD) | (mean and SD) | (mean and SD) | (mean and SD) | |||
| G | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.8 | Friedman test | < 0.0001 |
| R | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.0 ± 0.7 | < 0.0001 | |
| B | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.9 | < 0.0001 | |
| A | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 1.1 ± 0.8 | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 1.0 ± 0.9 | < 0.0001 | |
| S | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 1.1 ± 0.8 | 0.8 ± 0.8 | 0.6 ± 0.8 | < 0.0001 |
| Subscale | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | Test | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mean and SD) | (mean and SD) | (mean and SD) | (mean and SD) | |||
| A | 0.5 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | Friedman test | < 0.0001 |
| B | 0.8 ± 0.6 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | < 0.0001 | |
| C | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 2 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | < 0.0001 | |
| D | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 0.0691 |
References
- Bhatta S, Gandhi S, Ghanpur A. Etiology and presenting features of vocal cord paralysis: changing trends over the last two decades. Egypt J Otolaryngol. 2022;38. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s43163-022-00322-x
- Rosenthal L, Benninger M, Deeb R. Vocal fold immobility: a longitudinal analysis of etiology over 20 years. Laryngoscope. 2007;117:1864-1870. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e3180de4d49
- Sulica L, Rosen C, Postma G. Current practice in injection augmentation of the vocal folds: indications, treatment principles, techniques, and complications. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:319-325. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20737
- Walton C, Conway E, Blackshaw H. Unilateral vocal fold paralysis: a systematic review of speech-language pathology management. J Voice. 2017;31:509.e7-509.e22. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2016.11.002
- Marques J, Marronnier A, Crampon F. Early management of acute unilateral vocal fold paralysis: update of the literature. J Voice. 2021;35:924-926. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2020.02.021
- Brunings W. Uber eine neue behandlungsmethode der rekurrenslahmung. Verh Ver Laryngol. 1911;18:93-151.
- Lakhani R, Fishman J, Bleach N. Alternative injectable materials for vocal fold medialisation in unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009239.pub2
- Hertegård S, Hallén L, Laurent C. Cross-linked hyaluronan used as augmentation substance for treatment of glottal insufficiency: safety aspects and vocal fold function. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:2211-2219. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200212000-00016
- Wang C, Wu S, Tu Y. Hyaluronic acid injection laryngoplasty for unilateral vocal fold paralysis-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cells. 2020;9. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112417
- Ricci Maccarini A, Stacchini M, Mozzanica F. Efficacy of trans-nasal fiberendoscopic injection laryngoplasty with centrifuged autologous fat in the treatment of glottic insufficiency due to unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2018;38:204-213. doi:https://doi.org/10.14639/0392-100X-2012
- Ricci Maccarini A, De Rossi G, Pieri F. Injection Laryngoplasty. (Bergamini G, Presutti L, Molteni G, eds.). Springer International Publishing; 2015.
- Heman-Ackah Y, Heuer R, Michael D. Cepstral peak prominence: a more reliable measure of dysphonia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2003;112:324-333. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940311200406
- Barsties B, Maryn Y. External validation of the acoustic voice quality index version 03.01 with extended representativity. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2016;125:571-583. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/0003489416636131
- Fantini M, Ricci Maccarini A, Firino A. Validation of the Acoustic Voice Quality Index (AVQI) Version 03.01 in Italian. J Voice. 2023;37:631.e1-631.e6. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2021.02.029
- Hirano M. Disorders of Human Communication 5. Clinical Examination of Voice. (Arnold G, Winckel F, Wyke B, eds.). Springer-Verlag; 1981.
- Ricci-Maccarini A, Schindler A, Mozzanica F. Validity, reliability and reproducibility of the “Extended GRBAS Scale” a comprehensive perceptual evaluation of dysphonia. J Voice. 2022;39:393-402. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2022.09.008
- Ricci-Maccarini A, Mozzanica F, Fantini M. Validity, reliability and reproducibility of the VLS parameters form for the collection of videolaryngostroboscopic basic findings. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024;281:2489-2497. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-024-08480-9
- Forti S, Amico M, Zambarbieri A. Validation of the Italian Voice Handicap Index-10. J Voice. 2014;28:263.e17-263.e22. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2013.07.013
- Friedman A, Burns J, Heaton J. Early versus late injection medialization for unilateral vocal cord paralysis. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:2042-2046. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.21097
- Jeong G, Lee D, Lee Y. Treatment efficacy of voice therapy following injection laryngoplasty for unilateral vocal fold paralysis. J Voice. 2022;36:242-248. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2020.05.014
- Ballard D, Abramowitz J, Sukato D. Systematic review of voice outcomes for injection laryngoplasty performed under local vs general anesthesia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;159:608-614. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599818780207
- Kwon T, Buckmire R. Injection laryngoplasty for management of unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;12:538-542. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/01.moo.0000144393.40874.98
- Zeitels S, Lombardo P, Chaves J. Vocal fold injection of absorbable materials: a histologic analysis with clinical ramifications. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2019;128:71S-81S. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/0003489418805503
- Haddad R, Ismail S, Khalaf M. Lipoinjection for unilateral vocal fold paralysis treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2022;132:1630-1640. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.29965
- Miaśkiewicz B, Panasiewicz A, Nikiel K. Comparison of 24-month voice outcomes after injection laryngoplasty with calcium hydroxylapatite or hyaluronic acid in patients with unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2022;43. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103207
Downloads
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Copyright (c) 2025 Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria e chirurgia cervico facciale
How to Cite
- Abstract viewed - 869 times
- PDF downloaded - 228 times




